Solving Systems of ODEs#
Teng-Jui Lin
Content adapted from UW CHEME 375, Chemical Engineering Computer Skills, in Spring 2021.
Python skills and numerical methods
Solving ODE and systems of ODEs by
scipy.integrate.solve_ivp()
ChemE applications
Reaction kinetics
Chemical kinetics of one reaction#
Problem Statement. Given a first order reaction
Solve the system analytically and numerically using Euler’s method, given that the initial concentration of
Solution. We can solve the initial value problem analytically using separation of variables, having
Because we have an initial value of
Using Euler’s method, we can numerically solve the system with
through iterations.
Implementation#
In this approach, we use Euler’s method and scipy.integrate.solve_ivp() to solve the ODE.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.integrate import solve_ivp
def dCA_dt(k, CA):
return -k*CA
# known values
CA0 = 4 # M
k = 0.36 # min-1
t_final = 15 # min
dt = 0.5 # time step
# list of variables
t = np.arange(0, t_final+dt, dt)
CA_euler = np.zeros_like(t)
CA_euler[0] = CA0
# euler's method
for i in range(len(t)-1):
CA_euler[i+1] = CA_euler[i] + dt*dCA_dt(k, CA_euler[i])
def CA(k, t):
return 4*np.exp(-k*t)
CA_analytic = CA(k, t)
# plot settings
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'
%matplotlib inline
plt.rcParams.update({
'font.family': 'Arial', # Times New Roman, Calibri
'font.weight': 'normal',
'mathtext.fontset': 'cm',
'font.size': 18,
'lines.linewidth': 2,
'axes.linewidth': 2,
'axes.spines.top': False,
'axes.spines.right': False,
'axes.titleweight': 'bold',
'axes.titlesize': 18,
'axes.labelweight': 'bold',
'xtick.major.size': 8,
'xtick.major.width': 2,
'ytick.major.size': 8,
'ytick.major.width': 2,
'figure.dpi': 80,
'legend.framealpha': 1,
'legend.edgecolor': 'black',
'legend.fancybox': False,
'legend.fontsize': 14
})
# plot CA vs t
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(4, 4))
ax.plot(t, CA_euler, label='Euler')
ax.plot(t, CA_analytic, label='Analytic')
ax.set_title('$C_A(t)$')
ax.set_xlabel('$t \ [\mathrm{min}]$')
ax.set_ylabel('$C_A \ [\mathrm{M}]$')
ax.axis([0, t_final, 0, CA0])
ax.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x269446517c8>
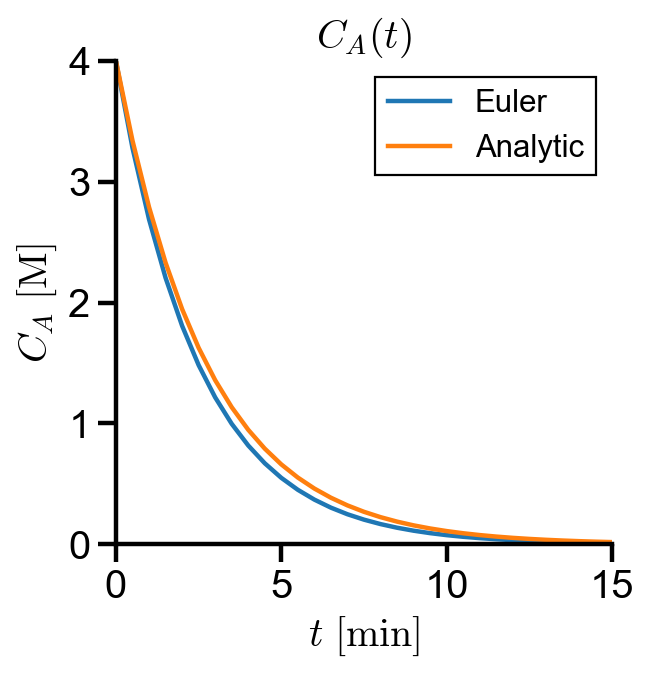
By inspection, we can see that there is error associated with Euler’s method.
Chemical kinetics of reaction networks#
Problem Statement. A batch reactor has a set of reactions
with concentrations governed by the system of ODEs
(a) Solve the concentration over time for 8 hours given initial concentration
(b) Determine the maximum concentration of
Solution. The system of ODEs is already in the form of solve_ivp() to solve for concentration over time.
Implementation#
In this approach, we use scipy.integrate.solve_ivp() to solve the system of ODEs.
def ODEsyst2(x, Y):
# x -> independent variable
# Y -> functions evaluated at independent variable
CA, CB, CC = Y
k1, k2 = [0.92, 0.08]
odes = np.array([
-k1*CA,
2*k1*CA - k2*CB**2,
0.5*k2*CB**2
])
return odes
domain = [0, 8]
initial_values = [10, 0, 0]
x_eval = np.arange(0, 8.1, 0.1)
soln = solve_ivp(ODEsyst2, domain, initial_values, t_eval=x_eval)
t = soln.t
CA, CB, CC = soln.y
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(4, 4))
ax.plot(t, CA, label='$C_A$')
ax.plot(t, CB, label='$C_B$')
ax.plot(t, CC, label='$C_C$')
ax.set_title('$C_i(t)$')
ax.set_xlabel('$t \ [\mathrm{h}]$')
ax.set_ylabel('$C_i \ [\mathrm{M}]$')
ax.set_xlim(0, 8)
ax.set_ylim(0, 10)
ax.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x2694477ec08>
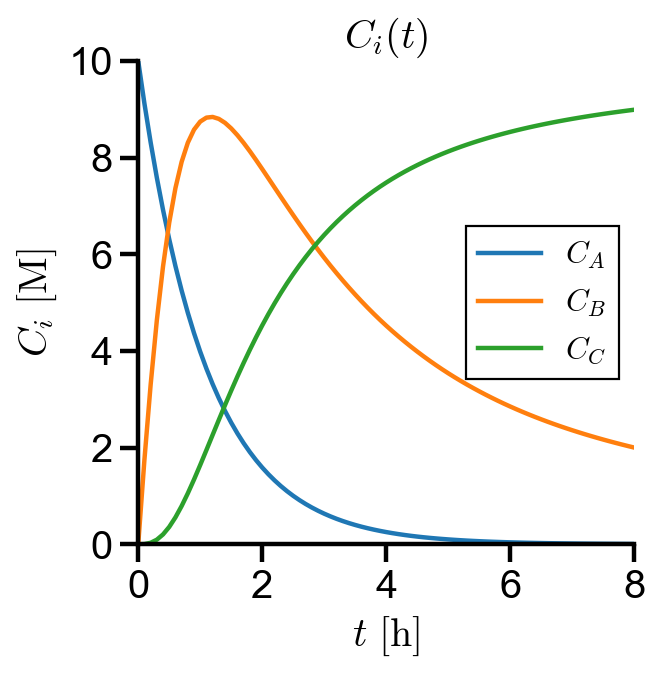
CB_max = CB.max()
CB_max
8.84376537393465
CB_max_time = t[CB.argmax()]
CB_max_time
1.2000000000000002
print(f'Maximum concentration of B = {CB_max:.2f} M')
print(f'Time when concentration of B is at maximum = {CB_max_time:.1f} h')
Maximum concentration of B = 8.84 M
Time when concentration of B is at maximum = 1.2 h

